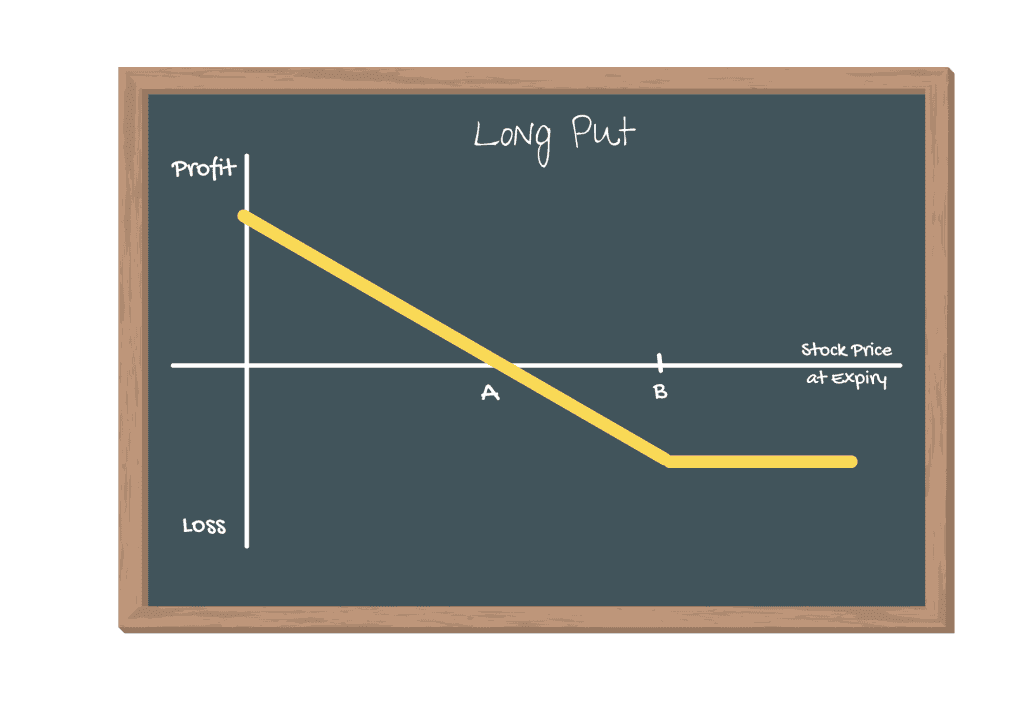
Description of the Long Put Strategy:
Buying a Put is the opposite of buying a call. A put is an option to sell. So, when you are buying a put you are expecting the price of the stock or underlying asset to go down.
ITM | In-the-money | Stock price < put strike price |
ATM | At-the money | Stock price = put strike price |
OTM | Out-of-the-money | Stock price > put strike price |
Steps to Trading:
- Buy the put option
Remember:
- Each contract gives you the option to buy the number of the underlying asset as per the lot size. For example, for the HDFC BANK, buying 1 lot gives you the option to buy 550 shares of HDFC BANK.
- Options for the indices like NIFTY or BANKNIFTY are cash-settled. That is, if your call option closes ITM, you will be credited the amount of the profit and vice versa for OTM options.
Rationale
In this trade, you are looking at making a better return than if you had simply shorted the stock itself. However, we need to make sure that we give ourselves enough time to be right. At least, 3 months, but ideally 6 months to a year. Although, the market for long-term options may not always be liquid, at least in the Indian market.
Another method is to buy only deep ITM Puts.
Advantages:
- Profit when the price of the stock or underlying asset falls
- Far greater leverage than simply shorting the stock
- Uncapped profit potential with limited risk
Disadvantages:
- The potential loss is 100% of your investment, if the strike price, expiration, and stock are badly chosen
- High leverage is a two-edged sword and can work against you if the stock price moves up. Ensure you have a risk management system in place.
Exiting the Position
- Sell the puts you bought
Mitigating a Loss:
- Set up your stop loss, entry price, and target (SET) using the underlying asset
Cost | Premium of the Put you buy |
Maximum Risk | Put premium |
Maximum Reward | Strike price minus premium received |
Break-even | Strike price minus Put Premium received |
Margin Required | No additional margin required besides the cost of the put |
Effects of Time decay | For this trade, time works against you. Especially in the week running up to expiry |
Effects of Volatility | After you are in the trade, you want the volatility to increase. This will increase the price of the put you bought. |
Expert Tips:
- Use Leverage wisely – although buying a Put Option cost substantially less than shorting the stock, you can still lose your entire investment. A general rule of thumb is to sell as many units of a Put Option as the number of units of the stock you can afford.
If you can short 100 units with your capital, buy 1 unit of Put (lot size 100).
If you can afford to short 200 units of the stock, buy 2 units of Puts.
- Buy ITM Put – In the Indian stock market, very far-month options are usually illiquid. This means that buying an ATM or OTM Put is not a good strategy, since time is not on your side. In this scenario, buying an ITM Put is a better strategy. ITM Puts are more expensive, but they are worth the money you pay for them.

