Description
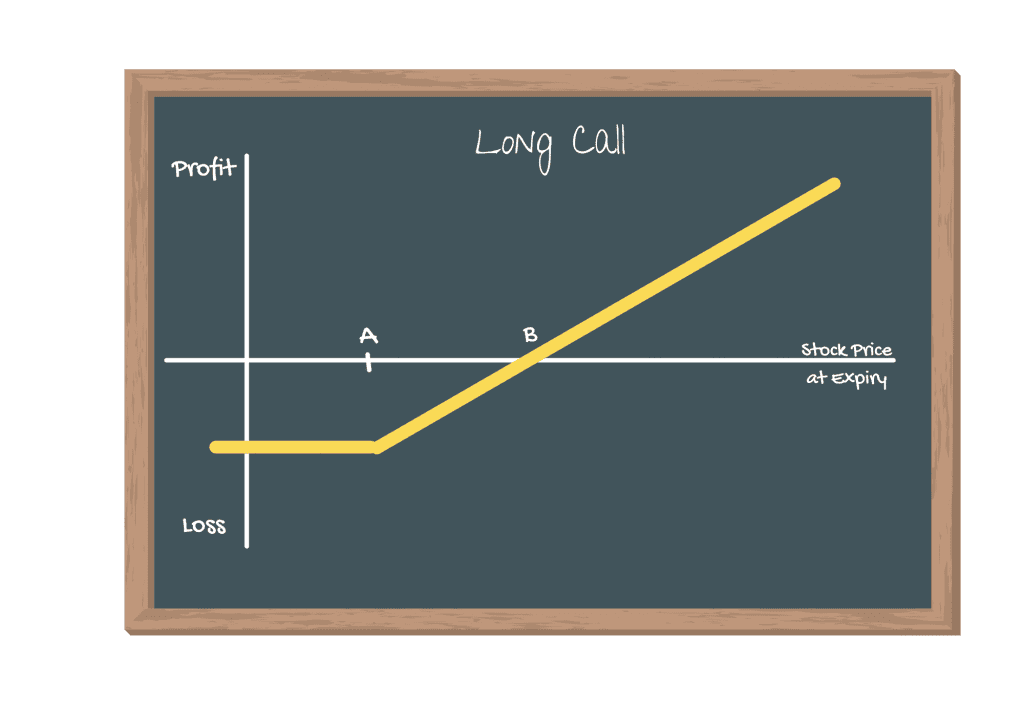
The long call strategy involves buying call options, betting on a stock’s increase. This allows investors to maximize potential gains while limiting risk to the premium paid.
Buying a call is one of the most basic of all options strategies. It is one of the first options trade you will take after gaining experience in buying and selling stocks.
A call is an option to buy, so obviously you are expecting the price of the underlying asset to rise.
ITM | In-the-money | Stock price > call strike price |
ATM | At-the money | Stock price = call strike price |
OTM | Out-of-the-money | Stock price < call strike price |
Steps to Trading the Long Call Strategy
- Buy the call option
Remember:
- Each contract gives you the option to buy the number of the underlying asset as per the lot size. For example, for the HDFC BANK, buying 1 lot gives you the option to buy 1,350 shares of HDFC BANK.
- Options for the indices like NIFTY or BANKNIFTY are cash-settled. That is, if your call option closes ITM, you will be credited the amount of the profit and vice versa for OTM options.
Rationale
To make a better return than simply buying the stock. However, we need to make sure that we give ourselves enough time to be right. At least, 3 months, but ideally 6 months to a year. Although, this market may not always be liquid, at least in the Indian market.
Another method is to buy only deep ITM Calls.
Advantages:
- Cheaper than buying the stock
- Uncapped profit potential with limited risk
Disadvantages:
- Potential 100% loss
- High leverage can be dangerous if the stock moves against you
Exiting the Position:
- Sell the call you bought
Mitigating a Loss:
- Set a stop loss as per your trade plan. This could be based on the price of the underlying asset or the price of the option itself.
Cost | Price of the call |
Maximum Risk | Call premium. 100% of your investment. |
Maximum Reward | Unlimited as the stock price rises |
Break-even | Strike price + Call Premium |
Margin Required | No additional margin required |
Effects of Time decay | Time is the enemy. Negative effect, especially in the week leading up to expiry |
Effects of Volatility | After you are in the trade, you want the volatility to increase. Increased volatility will increase the price of your Call Option. |
Expert Tips for Trading the Long Cal:
- Use Leverage wisely – although buying a Call Option costs substantially less than buying the stock, you can still lose your entire investment. A general rule of thumb is to buy as many units of a Call Option as the number of units of the stock you can afford.
If you can buy 100 units with your capital, buy 1 unit of Call (lot size 100).
If you can afford to buy 200 units of the stock, buy 2 units of Call.
Many traders use Call options for day-trading or swing trading. For this kind of trading, I always recommend you have a more comprehensive Risk Management system.
Read this article to understand how Risk Management works and how you can create your Risk Management strategy.
- Buy ITM Call – In the Indian stock market, very far-month options are usually illiquid. This means that buying an ATM or OTM Call is not a good strategy, since time is not on your side. In this scenario, buying an ITM Call is a better strategy. ITM Calls are more expensive, but they are worth the money you pay for them.
- Buying Call for Day Trading – Considering the nuances of the Indian Market, as discussed above, a popular strategy is to use call for day trading, as you would a stock. Use the charts of the Call itself to SET up your trades (Stop loss, Entry, Target). Options are usually more fast-paced than stocks since they control a larger asset. This provides for greater intraday gains. However, be careful of the volatility and have comprehensive risk management and market timing strategies.

